1.6 Acyclic Graph
A directed graph with no cycles is called directed acyclic graph or a DAG for short. An acyclic digraph has at least one vertex with an out-degree of zero.
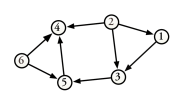
Figure 4 shows a variant of the directed graph of Figure 1 that contains no cycles. You will observe that vertex 4 has an out-degree of zero.
A directed tree is a connected DAG with the following properties:
-
There is one vertex, called the root, which no edges enter.
-
All vertices except the root have one entering edge.
-
There is a unique path from each vertex to the root.
A DAG consisting of one or more trees is called a forest. If the graph is a forest and the edge is in , vertex is the parent of and vertex is the child of . If there is a path from to , then vertex is an ancestor of and vertex is a descendent of . A vertex with no proper descendants is a leaf. A vertex and its descendants form a subtree of . The vertex is the root of this subtree. The depth of vertex is the length of the path from the root to . The height of vertex is the length of the longest path from to a leaf. The height of a tree is the height of its root. The level of vertex is its depth subtracted from the height of the tree.
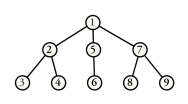
Figure 5 depicts a directed tree. Its root is vertex 1. Its leaves are the set of vertices .
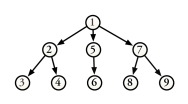
An undirected, connected, acyclic graph is called a free tree or an undirected tree. A rooted free tree is a free tree in which one vertex has been designated as the root. A directed tree is converted into a rooted free tree by discarding the orientation of the edges. A rooted free tree is converted into a directed tree by orienting each edge away from the root. The terminology which applies to directed trees also applies to rooted free trees.